Global Study Warns: 76% of People Need More Omega-3 for Better Health
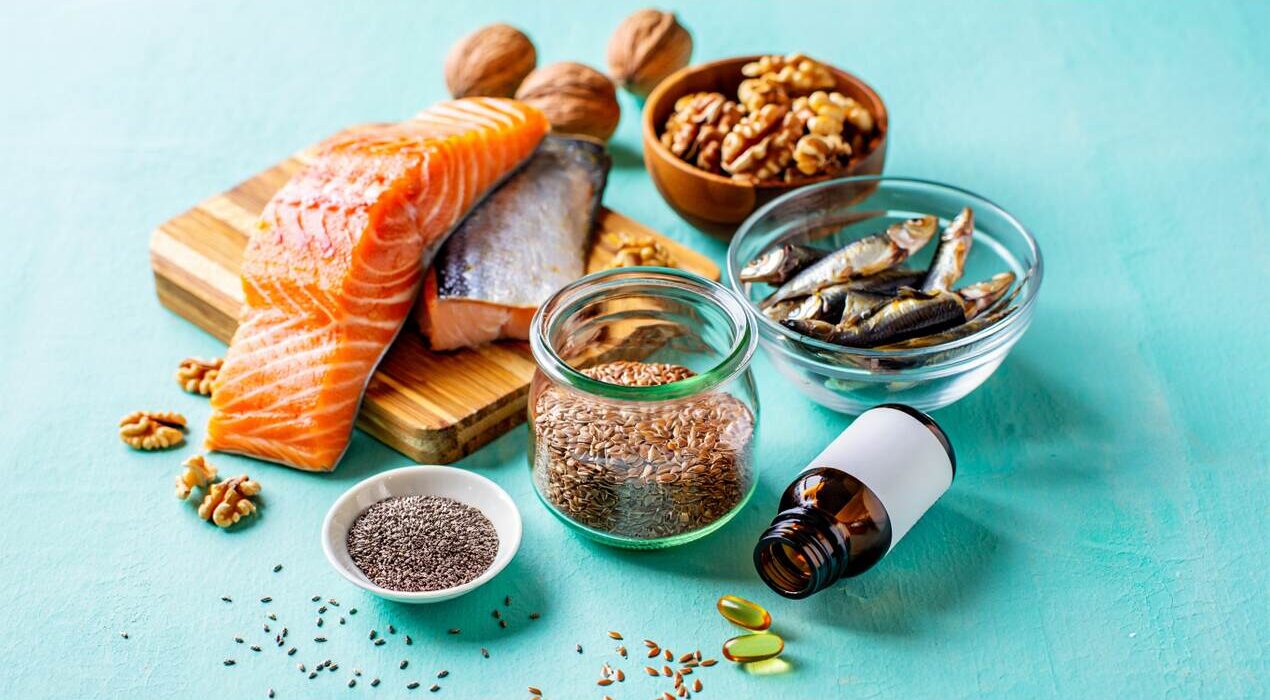
A major global review warns that most people still fall short on omega-3. The study, led by the University of East Anglia, the University of Southampton, and Holland & Barrett, shows that 76 percent of the world’s population consumes less than recommended levels. As a result, experts view this as a significant public health concern.Omega-3 fatty acids support the heart, brain, eyes, and immune system. They also help regulate inflammation. However, many people struggle to eat enough oily fish or plant-based sources to meet daily needs.
Why Omega-3 Matters at Every Age
Researchers note that EPA and DHA play vital roles throughout life. For example, they support early brain and eye development in infants. They also help maintain heart and cognitive health in adults. In addition, higher omega-3 levels may reduce the risk of depression and age-related decline.The review also highlights that many people need supplements to reach recommended levels, especially during pregnancy or when fish intake is low. Therefore, experts encourage simple and sustainable options, such as fortified foods or algae-based supplements.
Global Guidelines Still Don’t Match
The authors found a major mismatch between scientific evidence, national guidelines, and what people actually consume. Guidance varies widely between countries, which creates confusion. This new review aims to provide clearer direction and encourage consistent standards across the world.Most adults need about 250 mg of combined EPA and DHA each day. Pregnant individuals need an extra 100–200 mg of DHA. People can meet these targets by eating more oily fish, such as salmon or mackerel. Supplements offer another reliable option when dietary intake is limited.The researchers hope this publication helps guide future nutrition policy. They also believe it will support healthcare professionals, food manufacturers, and global communities working to improve long-term health.