Transforming Air into Fuel and Fertilizer with a New 2D Material
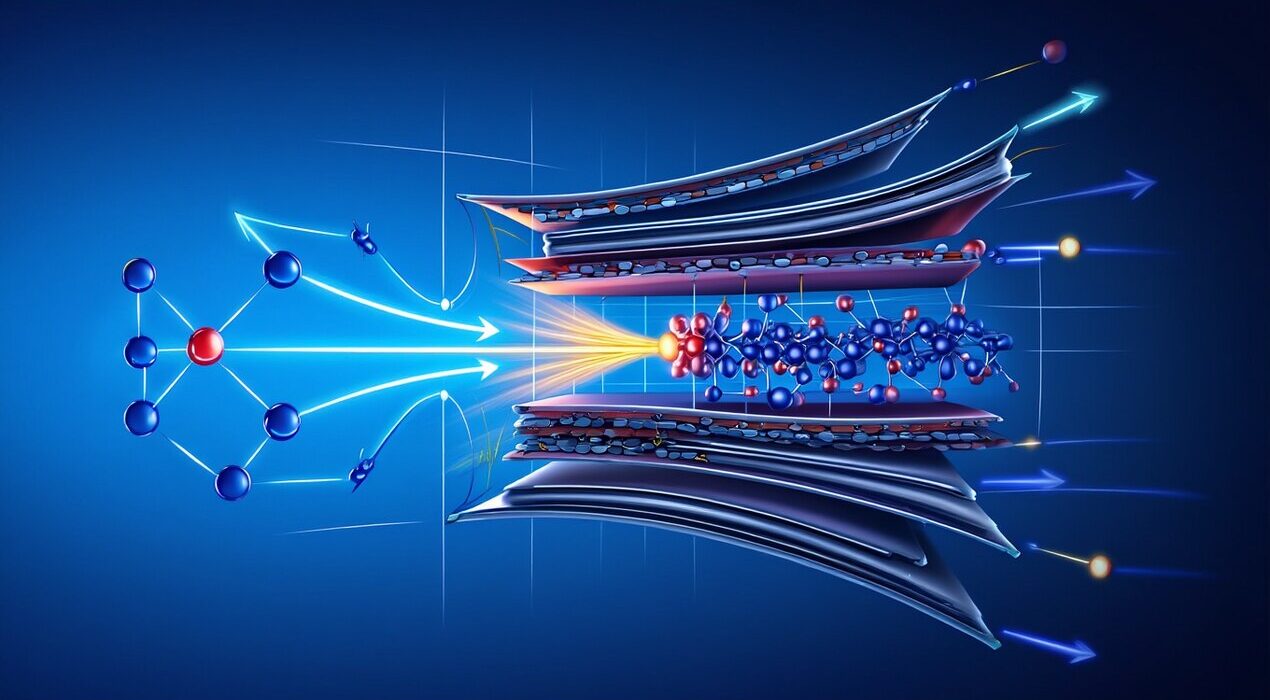
Researchers unveiled a new 2D material that lets us turn air into fuel and fertilizer. The material belongs to the family called MXenes and it features ultra-thin, two-dimensional sheets. In addition, scientists found they can tune atomic properties for better performance.
A Game-Changing Material
The study shows that this 2D material can take components from the air and convert them into ammonia. Ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers and it can also act as a fuel. Therefore, this discovery could reshape how we approach energy and agriculture.
How It Works and Why It Matters
The team at Texas A&M University used nitride-based MXenes and measured how nitrogen atoms in the lattice react under certain conditions. For example, by changing how nitrogen sits in the material they adjusted vibrational properties that affect catalytic activity.
In addition, the material’s ability to fine-tune its chemistry means it may replace expensive catalysts. The conversion from air to useful chemicals can happen under greener settings rather than high-temperature, high-pressure methods. As a result, we could see lower cost and lower-impact production of fuel and fertilizer
Broader Impacts and Next Steps
This innovation could help agriculture become more sustainable. Farmers could one day access fertilizers made locally using ambient air rather than relying on big factories. Also, cleaner fuel production might reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and cut emissions.However, the technology still faces hurdles. Researchers need to test durability, scalability and real-world performance. In addition, regulatory and supply-chain factors will play a big role.
With the key phrase “air into fuel fertilizer”, we capture the essence of this breakthrough. This 2D material offers hope for a greener, more efficient future in both energy and food production. Stay tuned as the science progresses toward practical applications.