Tattoos Linked to Melanoma Risk: What Study Reveals
For many people, tattoos are a form of self-expression and identity. They allow individuals to feel more comfortable in their skin and showcase personal stories. However, recent research suggests that getting inked might have unexpected health implications.
The Study Findings
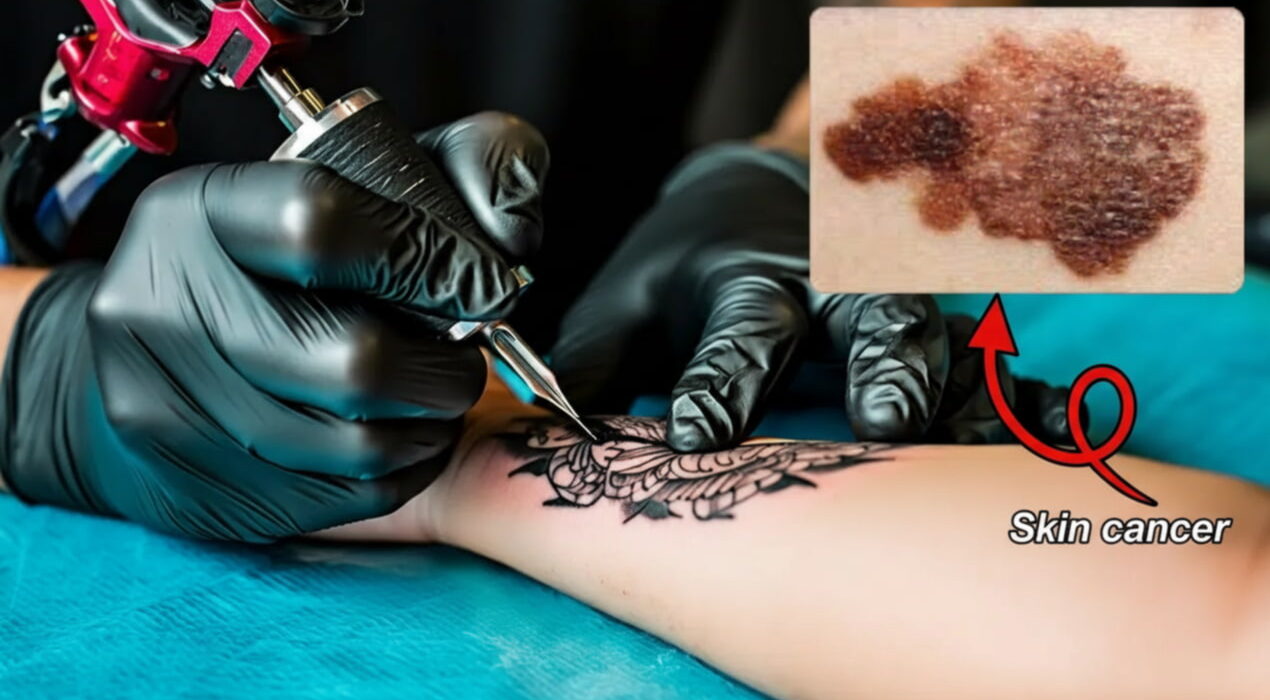
Researchers at Lund University found that people with tattoos had a 29% higher risk of developing melanoma, a serious skin cancer linked to UV exposure. Surprisingly, tattoos did not increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma, another UV-related cancer. Scientists say the difference comes from how these cancers develop from different cell types. The study analyzed medical records and surveyed over 11,000 participants about their tattoo history, including size, location, and age at first tattoo. Interestingly, the risk of melanoma seemed higher in people who had tattoos for over ten years, though more research is needed to confirm this.
What This Means for You
Does this mean tattoos directly cause melanoma? Experts say it’s too early to tell. While there is a possible link, one study cannot prove causation. Factors like chronic inflammation, chemical breakdown of tattoo pigments, and UV exposure may play a role. Tattoo ink varies widely, and some pigments may produce harmful by-products when exposed to sunlight or during laser removal. Understanding these processes is crucial for assessing long-term health risks. For now, people with tattoos should monitor their skin regularly and follow sun-safety measures. Dermatologists recommend consulting a professional if any changes or unusual marks appear. Staying informed and taking preventive steps can help minimize potential risks while enjoying your body art.